This post presents our quarterly update of the economic forecasts generated by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) model. We describe very briefly our forecast and its change since February 2017. As usual, we wish to remind our readers that the DSGE model forecast is not an official New York Fed forecast, but only an input to the Research staff’s overall forecasting process. For more information about the model and variables discussed here, see our
DSGE Model Q & A.
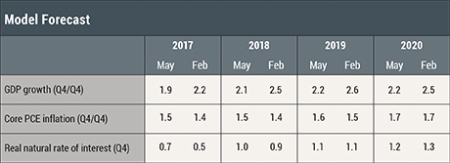
The table and charts below show the May model forecasts for 2017-20 alongside the forecasts produced in February. The May projections use quarterly macroeconomic data released through the first quarter of 2017, augmented with the FRBNY staff forecasts for GDP growth and core PCE inflation for the second quarter of 2017 and with available financial data through April 30, 2017.
How did the forecasts change since February?
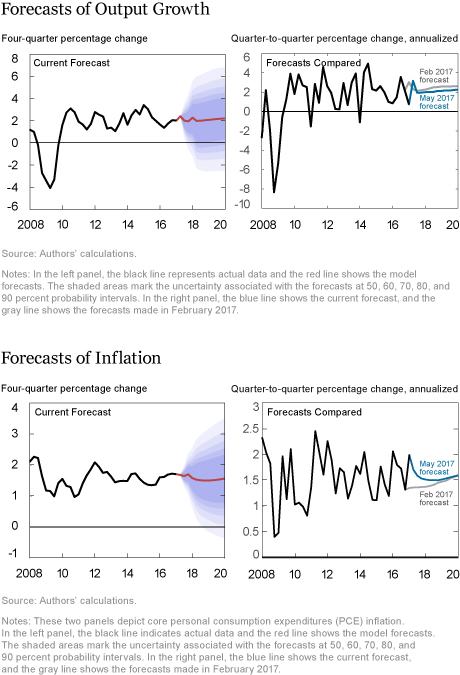
• The current GDP growth forecast is somewhat weaker than its February counterpart throughout the forecast horizon. For 2017 the change in the forecast primarily reflects slower-than-expected expansion in the first quarter. GDP is now expected to grow at 1.9 percent in 2017 (in Q4/Q4 terms) and accelerate only modestly in the following years.
• The lower forecast for GDP growth relative to February is mainly due to a lower projected path for productivity growth. This negative force is partly counteracted by low credit spreads between Baa corporate and Treasury securities, a trend that should support activity in the short and medium run.
• The core PCE inflation forecast is slightly higher than in February, which is not surprising in light of the decline in productivity. The uptick in core PCE in the first quarter of 2017 pushes the core inflation outlook up to 1.5 percent (Q4/Q4) in 2017. Inflation is projected to increase gradually to 1.7 percent (Q4/Q4) in 2020.
• The projections for both output and core PCE are surrounded by considerable uncertainty.
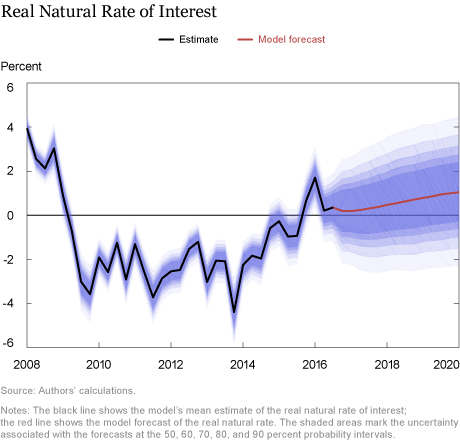
• The forecast for the real natural rate of interest—the real rate of interest that would prevail in the economy absent nominal rigidities and markup shocks—has been revised up by 20 and 10 basis points in 2017 and 2018, respectively (see the chart below). The primary reason for the revision was that the decrease in credit spreads that occurred in the fourth quarter of 2016 turned out to persist in the first and second quarters of 2017, leading to increased estimates of the natural rate and a higher jump-off point for the forecast (recall that the natural rate of interest is not directly observable). Going forward, the natural rate of interest is projected to continue to increase, albeit at a slow pace.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this post are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the responsibility of the authors.

Ozge Akinci is an economist in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Marco Del Negro is a vice president in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.
 Abhi Gupta is a senior research analyst in the Group.
Abhi Gupta is a senior research analyst in the Group.
 Pearl Li is a senior research analyst in the Group.
Pearl Li is a senior research analyst in the Group.

Erica Moszkowski is a senior research analyst in the Group.
How to cite this blog post:
Ozge Akinci, Marco del Negro, Abhi Gupta, Pearl Li, and Erica Moszkowski, “The New York Fed DSGE Model Forecast—May 2017,” Federal Reserve Bank of New York Liberty Street Economics (blog), May 31, 2017, http://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2017/05/the-new-york-fed-dsge-model-forecast-may-2017.html.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics