Cryptocurrencies’ market capitalization has grown rapidly in recent years. This blog post analyzes the role of macro factors as possible drivers of cryptocurrency prices. We take a high-frequency perspective, and we focus on Bitcoin since its market capitalization dwarfs that of all other cryptocurrencies combined. The key finding is that, unlike other asset classes, Bitcoin has not responded significantly to U.S. macro and monetary policy news. This disconnect is puzzling, as unexpected changes in discount rates should, in principle, affect the price of Bitcoin.
Background
Prior to its recent decline, the market value of cryptocurrencies reached a staggering $2.5 trillion, with Bitcoin crossing the $1 trillion mark. In addition, Bitcoin represents the lion’s share—between 50 percent (nowadays) and 90 percent (in 2016)—of the overall capitalization of the digital currency market.
Market Capitalization of Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies
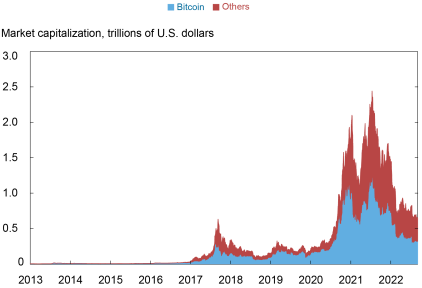
Notes: The chart plots the market capitalizations of Bitcoin and twenty-two other cryptocurrencies (Aave, BinanceCoin, Cardano, ChainLink, Cosmos, CyrptocomCoin, Dogecoin, EOS, Ethereum, Iota, Litecoin, Monero, NEM, Polkadot, Solana, Stellar, Tether, Tron, Uniswap, USDCoin, WrappedBitcoin, and XRP). Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the total number of coins in circulation by their price.
Given their growing relevance, it is natural to study the drivers of cryptocurrency prices. This blog post focuses on macroeconomic news and monetary policy surprises. We interpret cryptocurrencies as assets whose current price should depend on the expected discounted value of future values. This characterization implies that, from a macroeconomic point of view, developments that influence current and future interest rates, whether directly (news about monetary policy) or indirectly (news about macroeconomic conditions), should affect the value of cryptocurrencies.
We use a novel and comprehensive intraday data set to identify the effects of this news. By relying on high-frequency data in a short enough window around a macro announcement, the data release is (most likely) the only information systematically hitting the market. Hence, by looking at the response of asset prices in that time window around various announcements, this blog post conducts the empirical finance version of a natural experiment.
As an example, the chart below shows the response of several U.S. asset prices around two types of news releases: news about the real economy, such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Employment Situation report (left panel), and news about monetary policy, specifically the FOMC meeting (right panel). The June 2016 labor market report contained a lower-than-expected nonfarm payrolls figure, as compared to the Bloomberg consensus. Consequently, the dollar immediately depreciated against the euro by about 1 percent, stock prices declined by about 0.5 percent, and gold prices increased by 2 percent. Bitcoin, on the other hand, moved sideways. At the June 2021 Fed meeting, the FOMC signaled that interest rates needed to rise sooner and faster than market participants had anticipated. Again, the dollar, gold, and stock prices immediately responded to the release, but Bitcoin did not respond in a systematic manner.
Response of U.S. Asset Prices to Macroeconomic and Monetary Policy News
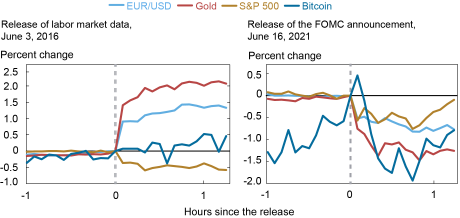
Notes: Responses are normalized at zero at the time of the news release. The horizontal axis displays the hours before/after the release. EUR/USD refers to the euro/dollar exchange rate, defined as the amount of U.S. dollars needed to buy one euro.
Analysis and Results
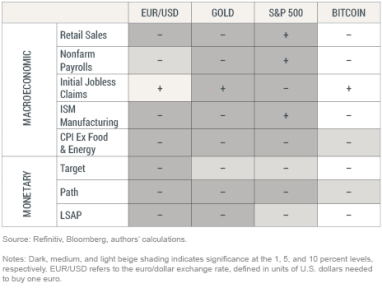
We systematically analyze the response of the EUR/USD exchange rate, gold, the S&P 500, and Bitcoin to ten sets of macro announcements that have been singled out as important in the academic literature. In studying the responses of selected asset prices to macroeconomic and monetary policy news, we focus on the 2000-2022 period for all assets except Bitcoin, for which we chose a restricted (more meaningful) sample starting from 2017. (For more details on the analysis, see our related Staff Report on the topic.) We collect different pieces of macro news, covering the real economy and inflation, as well as monetary policy surprises. For monetary policy news, we consider three distinct dimensions. The first indicator, Target, captures unanticipated changes in the current federal funds rate target. The second indicator, Path, captures unanticipated changes in the future path of policy. The third indicator, LSAP, captures unanticipated announcements of future large‐scale asset purchases.
Our priors are based on a simple asset pricing model for Bitcoin. We model Bitcoin as an asset with no intrinsic value whose current value depends on the discounted value of its future price (for our beloved wonks, a “stochastic bubble”). We also accommodate the possibility of the asset having no value with a probability that depends positively on current and future interest rates. Since monetary policy news affects both current and future interest rates, it should be associated with Bitcoin valuation, while macroeconomic news has an indirect impact through the monetary policy reaction function.
By relying on the regressions’ estimates, we can test to what extent the response of an asset price to a given macroeconomic announcement is systematic. The table below reports the relationship between assets (columns) and selected macroeconomic and monetary news (rows). The shading indicates whether the response is systematic, with darker colors corresponding to more statistically significant effects. The symbol inside each cell indicates the sign of the correlation between asset returns and news. We find that the EUR/USD exchange rate, gold, and the S&P 500 significantly react to most macro and monetary news. In stark contrast, the response of Bitcoin is muted, and never significant at the 1 percent level even when we focus on just monetary policy news.
Comparing Asset Price Responses to News Events
Conclusions
So… is macroeconomic news driving Bitcoin? In this post, we conduct a systematic analysis of the impact of macroeconomic and monetary policy news on Bitcoin’s price. In contrast to exchange rates and stocks, Bitcoin is largely unresponsive to macro news. More puzzling is the result that Bitcoin does not also react to monetary policy surprises. At face value, our study casts some doubts on the role of discount rates in pricing Bitcoin. Given the short sample used in the analysis, the jury is still out on this one, and more evidence is needed to put the case to rest.

Gianluca Benigno is the head of International Studies in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group and a professor of economics at the University of Lausanne.
Carlo Rosa is an assistant professor at the University of Parma (Italy).
How to cite this post:
Gianluca Benigno and Carlo Rosa, “Is There a Bitcoin–Macro Disconnect?,” Federal Reserve Bank of New York Liberty Street Economics, February 8, 2023, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2023/02/is-there-a-bitcoin-macro-disconnect/
BibTeX: View |
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the responsibility of the author(s).














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics