Beverly Hirtle
Large bank holding companies (BHCs) continued to pay dividends to their shareholders well after the onset of the recent financial crisis. Academics, industry analysts, and policymakers have noted that these payments reduced capital at these firms at a time when there was considerable uncertainty about the full extent of losses facing individual banks and the banking industry. But dividends are not the only means to return capital to shareholders; stock repurchases serve much the same function. In this post, I examine common stock repurchases by large BHCs during the financial crisis and show that they behaved very differently from common stock dividends during the same period. While dividends remained relatively constant through late 2008, common stock repurchases dropped quickly after the beginning of the financial crisis, consistent with their historically tighter sensitivity to current performance and financial conditions.
BHC Dividends during the Financial Crisis
Many analysts and researchers have noted that large BHCs did not reduce common stock dividends until the financial crisis was well under way. For instance, in a study examining capital at large U.S. and European banks, securities firms, and U.S. government-sponsored enterprises, Acharya, Gujral, Kulkarni, and Shin show that dividends at these firms did not decrease significantly until early 2009. In an October 2008 New York Times op-ed piece, Scharfstein and Stein argued that dividend payments by the largest U.S. BHCs would “redirect more than $25 billion of the $125 billion [in TARP capital] to shareholders in the next year alone.” Both sets of authors argued that continued high dividend payments undercut the capitalization of the U.S. banking industry during a time of stress. In 2011, the Federal Reserve implemented the Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR) to review planned dividend payments and other capital distributions by large BHCs to ensure that they would retain sufficient capital to withstand stressed economic and financial market conditions even after making such distributions to shareholders (see my earlier post for a description of how the CCAR addresses this objective).
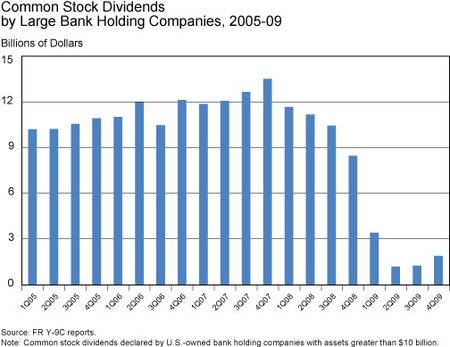
Regulatory report data confirm the findings about dividends from these earlier studies. The first chart (below) shows the quarterly history of dividends declared by large U.S. BHCs—those with at least $10 billion in assets—from 2005 to the end of 2009. This period starts two years before the onset of the crisis in mid-2007 and extends until the beginning stages of the recovery at the end of 2009. (For consistency over the period, the sample excludes the large nonbank financial firms that became BHCs in early 2009.) As the chart shows, large BHCs made dividend payments in the range of $9 billion to $12 billion per quarter from 2005 to 2007, and while dividends declined over the course of 2008, they did not fall significantly below this level until early 2009, more than a year into the financial crisis.
Dividends Are Not the Whole Story
Focusing just on dividends misses an important part of the story, however. Stock repurchases—when a company buys its own common stock in public or private markets or by tender offer—are another important way that a firm can return capital to shareholders. Like dividend payments, stock repurchases disperse cash from the company to shareholders. Moreover, repurchases reduce the amount of common stock outstanding one-for-one, just as dividend payments do. Dividend payments reduce retained earnings and thus reduce (potential) common equity, while stock repurchases are a direct reduction in the outstanding amount of common equity.
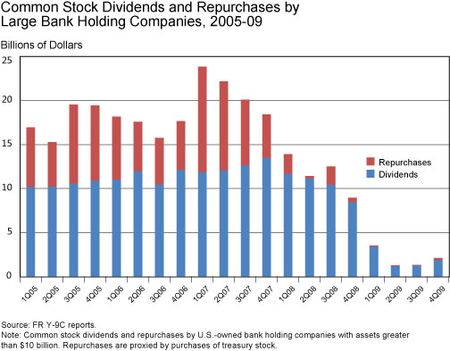
The second chart (below) updates the first one to include common stock repurchases for the sample of large BHCs. Both dividend and repurchase information come from the quarterly FR Y-9C regulatory reports, which contain balance sheet and income statement information for BHCs. While the Y-9C reports collect dividends declared as a distinct line item, repurchases are not reported directly and must be inferred from other information contained in the report. For the second chart, I’ve used BHC purchases of treasury stock—common stock issued but not held by the public—as a proxy for common stock repurchases. This is a noisy measure of repurchases, as it may omit some repurchase activity that is reported as part of other Y-9C line items. However, it is a reasonable proxy that should capture the broad movements in repurchase activity.
The second chart illustrates several notable aspects of repurchase activity by large BHCs. First, in the period leading up to the financial crisis, stock repurchases were significant, averaging $7.5 billion per quarter and peaking at $12 billion in the first quarter of 2007. Stock repurchases were about two-thirds the size of dividend payments over this period, meaning that total distributions to shareholders were substantially higher than indicated by considering dividends alone. This is not something new in the banking industry. Some of my earlier research, which examined BHC stock repurchases during the 1990s, also found that stock repurchases rivaled dividends as a way for BHCs to return capital to shareholders. Second, share repurchases dropped sharply during the early phases of the financial crisis, several quarters before dividends were significantly reduced. Stock repurchases by large BHCs fell from their peak of $12 billion in the first quarter of 2007 to about $2 billion during the first quarter of 2008, and were at negligible levels after the middle of that year. As noted above, dividends did not decrease significantly until early 2009.
Because of the decline in repurchases, large BHCs’ overall capital distributions to shareholders declined steadily over the course of 2007 and 2008, a somewhat different picture than the one that emerges by looking at dividends alone. By the beginning of 2008, overall capital distributions had fallen below the levels that prevailed during the pre-crisis period. Even so, as the second chart illustrates, it was not until early 2009, when dividends also declined sharply, that overall distributions fell to the very low levels that ultimately prevailed for the remainder of the financial crisis and the period that followed.
Why Are Repurchases Different?
Why did stock repurchases fall earlier and more sharply than dividend payments? Part of the explanation is likely owing to the differing nature of dividends and share repurchases. Dividends are publicly visible actions requiring regular authorization by a firm’s board of directors. In the banking industry, large BHCs typically declare dividends quarterly and announced them publicly in press releases. In contrast, for all firms, stock repurchases are much less transparent. Firms have the ability to select the timing and amount of repurchases flexibly over time, subject to the details of their repurchase programs. Research on nonfinancial firms has documented that stock repurchases generally vary more over time than dividends, with repurchases used more frequently by firms with volatile earnings, especially following periods of higher-than-expected profitability. My earlier research on repurchases in the banking industry in the 1990s also found that repurchases seemed to rise following periods of higher-than-average financial performance. In contrast, dividends tend to be interpreted as signals of long-term profitability, decreasing only when profits seem likely to fall to a lower level for a sustained period of time.
Much further research is needed to come to a full understanding of the decisions BHCs made regarding dividend and repurchase activity during the financial crisis. The charts in this post and the results of previous research provide some insight, but there is significant room to explore issues such as concerns about signaling financial weakness during a time of uncertainty, the role of herding behavior in the timing and extent of dividend reductions, and the relative impact of market-wide versus firm-specific factors in decisions to cut back on stock repurchases. And, looking ahead, supervisory oversight via the CCAR and the adoption of new regulatory capital standards that explicitly require reductions in capital distributions as regulatory capital ratios fall below certain trigger points will significantly affect BHCs’ decisions about capital distributions. In sum, it is important to consider both dividends and stock repurchases in order to understand the impact of capital distributions on the banking industry, since large BHCs actively use both to manage their capital and distribute cash to shareholders.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this post are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the responsibility of the author.
 Beverly Hirtle is a senior vice president in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.
Beverly Hirtle is a senior vice president in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics