
This post presents an update of the economic forecasts generated by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) model. We describe very briefly our forecast and its change since September 2024. As usual, we wish to remind our readers that the DSGE model forecast is not an official New York Fed forecast, but only an input to the Research staff’s overall forecasting process. For more information about the model and variables discussed here, see our DSGE model Q & A.
The New York Fed model forecasts use data released through 2024:Q3, augmented for 2024:Q4 with the median forecasts for real GDP growth and core PCE inflation from the November release of the Philadelphia Fed Survey of Professional Forecasters (SPF), as well as the yields on 10-year Treasury securities and Baa-rated corporate bonds based on 2024:Q4 averages up to November 22. Starting in 2021:Q4, the expected federal funds rate (FFR) between one and six quarters into the future is restricted to equal the corresponding median point forecast from the latest available Survey of Primary Dealers (SPD) in the corresponding quarter. For the current projection, this is the November SPD.
Once again, both professional forecasters and the DSGE model were surprised by the strength of the economy. Output growth in 2024:Q3 was more than 1 percentage point higher than the SPF had predicted in August—and therefore higher than the DSGE forecast, since the model used the SPF projection as a nowcast. In addition, the current SPF nowcast for annualized GDP growth in 2024:Q4 is also almost 2 percentage points higher than the DSGE prediction in September. Both forecast errors translate into higher output growth for 2024 and 2025 relative to September (2.6 versus 1.8 percent, and 1.7 versus 1.0 percent, respectively), but have less impact on the output projections thereafter (the current forecasts are 0.4 and 0.9 percent in 2026 and 2027 versus 0.8 and 1.3 percent in September). The probability of a recession, defined as four-quarter output growth falling below -1 percent over the next four quarters, has decreased from 31 percent in September to 24 percent now.
The model attributes much of the recent strength in the economy to monetary policy, which has become substantially less restrictive than predicted in September (recall that in September, the model used the July SPD to form policy expectations). Importantly, in terms of assessing the policy stance, the model’s prediction for the short-run real natural rate of interest, r*, has not changed for 2024 (2.4 percent) but its predictions are lower than they were in September for the remainder of the forecast horizon. The current forecast for r* is 2.1, 1.8, and 1.5 percent in 2025, 2026, and 2027, compared to 2.3, 1.9, and 1.6 percent in September.
Because the higher-than-predicted output is largely attributed to policy, as opposed to shocks that would raise potential output, the output gap is also estimated to be higher than it was in September.
Core PCE inflation forecasts are essentially the same as in September. Specifically, the current inflation projections are 2.7, 1.9, 1.8, and 1.9 percent in 2024, 2025, 2026, and 2027, versus 2.8, 1.8, 1.8, and 1.8 percent in September, respectively. While the less restrictive monetary policy pushes up inflation projections, according to the model, this is offset by higher productivity growth.
Forecast Comparison
| Forecast Period | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date of Forecast | Dec 24 | Sep 24 | Dec 24 | Sep 24 | Dec 24 | Sep 24 | Dec 24 | Sep 24 |
| GDP growth (Q4/Q4) | 2.6 (2.2, 3.0) | 1.8 (0.1, 3.6) | 1.7 (-3.4, 6.9) | 1.0 (-4.2, 6.3) | 0.4 (-4.7, 5.4) | 0.8 (-4.4, 6.2) | 0.9 (-4.6, 6.2) | 1.3 (-4.2, 6.7) |
| Core PCE inflation (Q4/Q4) | 2.7 (2.6, 2.8) | 2.8 (2.5, 3.0) | 1.9 (1.0, 2.6) | 1.8 (1.0, 2.5) | 1.8 (0.9, 2.7) | 1.8 (0.8, 2.7) | 1.9 (0.8, 2.9) | 1.8 (0.8, 2.9) |
| Real natural rate of interest (Q4) | 2.4 (1.3, 3.5) | 2.4 (1.2, 3.6) | 2.1 (0.7, 3.5) | 2.3 (0.9, 3.7) | 1.8 (0.2, 3.3) | 1.9 (0.3, 3.4) | 1.5 (-0.1, 3.1) | 1.6 (-0.1, 3.2) |
Notes: This table lists the forecasts of output growth, core PCE inflation, and the real natural rate of interest from the December 2024 and September 2024 forecasts. The numbers outside parentheses are the mean forecasts, and the numbers in parentheses are the 68 percent bands.
Forecasts of Output Growth
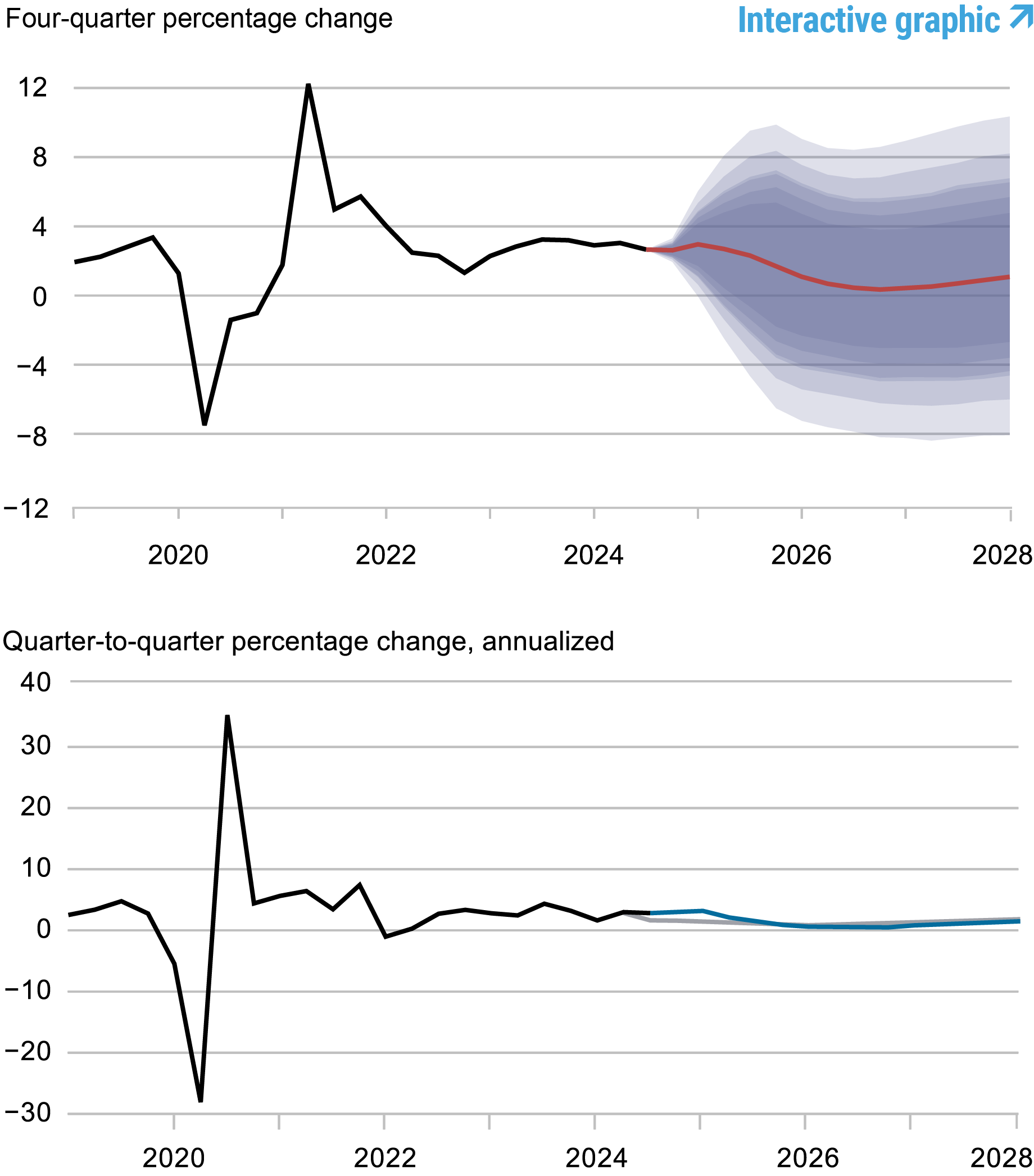
Source: Authors’ calculations.
Notes: These two panels depict output growth. In the top panel, the black line indicates actual data and the red line shows the model forecasts. The shaded areas mark the uncertainty associated with our forecasts at 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90 percent probability intervals. In the bottom panel, the blue line shows the current forecast (quarter-to-quarter, annualized), and the gray line shows the September 2024 forecast.
Forecasts of Inflation
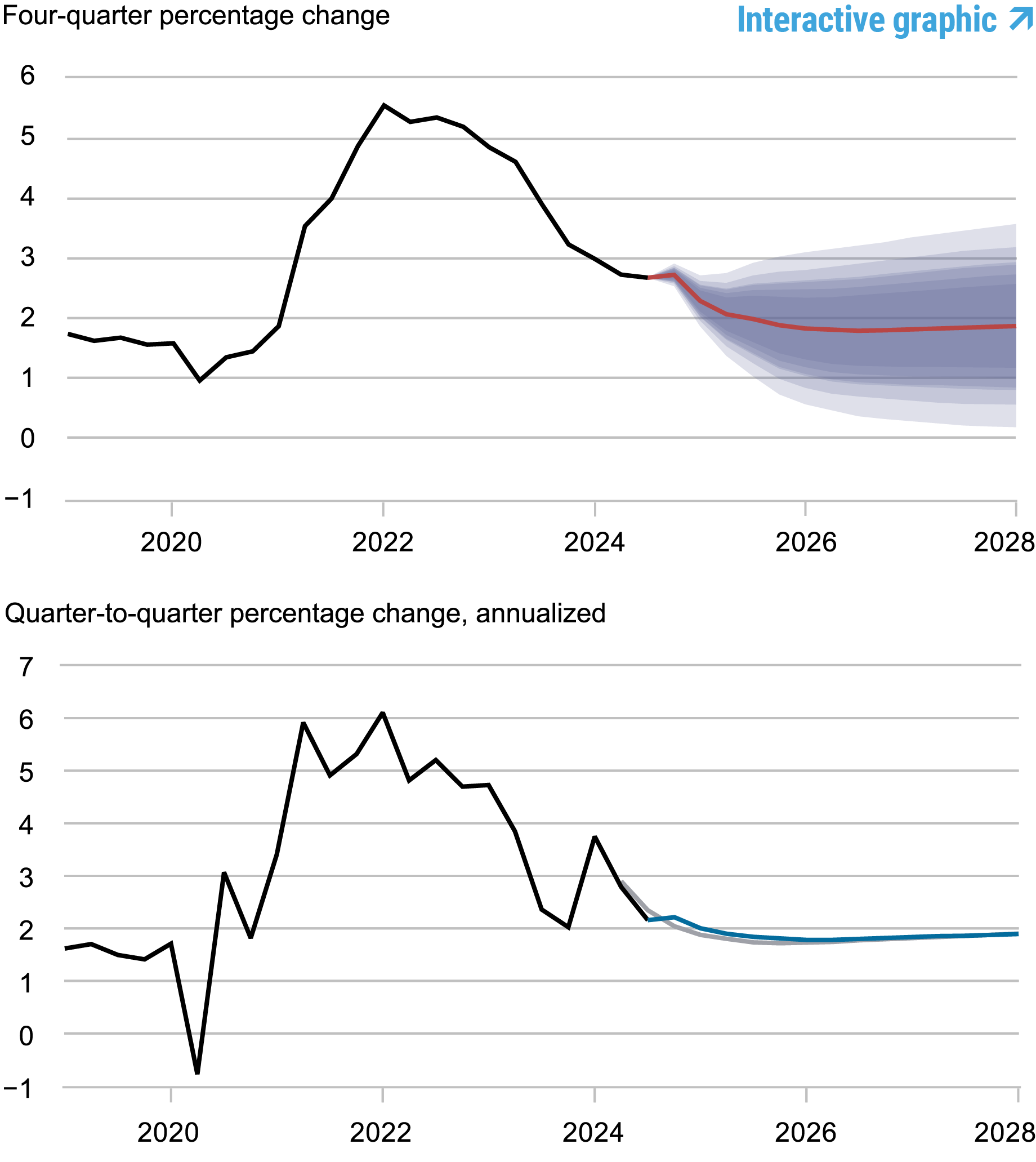
Source: Authors’ calculations.
Notes: These two panels depict core personal consumption expenditures (PCE) inflation. In the top panel, the black line indicates actual data and the red line shows the model forecasts. The shaded areas mark the uncertainty associated with our forecasts at 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90 percent probability intervals. In the bottom panel, the blue line shows the current forecast (quarter-to-quarter, annualized), and the gray line shows the September 2024 forecast.
Real Natural Rate of Interest
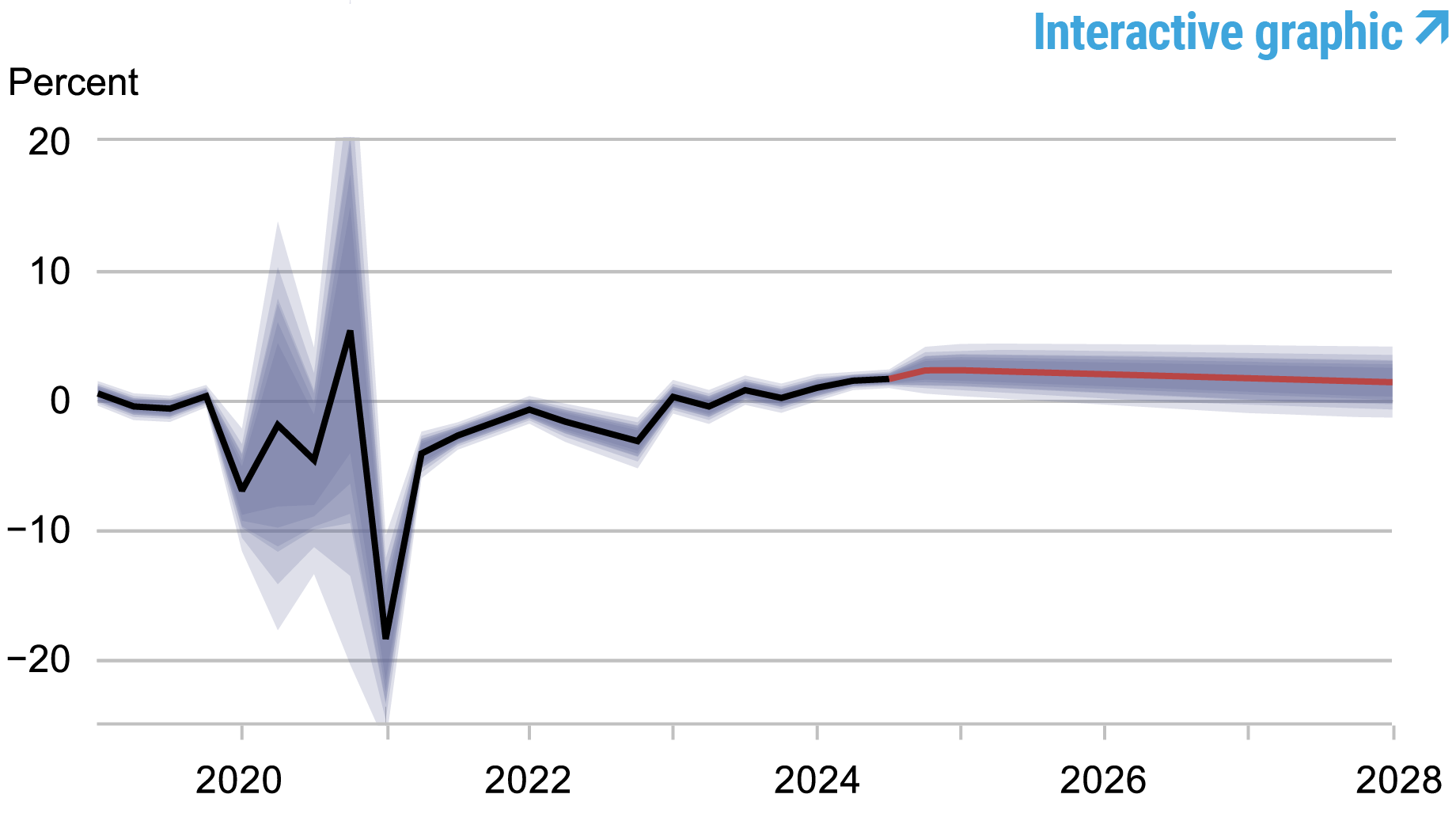
Source: Authors’ calculations.
Notes: The black line shows the model’s mean estimate of the real natural rate of interest; the red line shows the model forecast of the real natural rate. The shaded area marks the uncertainty associated with the forecasts at 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90 percent probability intervals.

Sophia Cho is a research analyst in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Marco Del Negro is an economic research advisor in Macroeconomic and Monetary Studies in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Ibrahima Diagne is a research analyst in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics. Group.

Pranay Gundam is a research analyst in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Donggyu Lee is a research economist in Macroeconomic and Monetary Studies in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Brian Pacula is a research analyst in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.
How to cite this post:
Sophia Cho, Marco Del Negro, Ibrahima Diagne, Pranay Gundam, Donggyu Lee, and Brian Pacula, “The New York Fed DSGE Model Forecast—December 2024,” Federal Reserve Bank of New York Liberty Street Economics, December 20, 2024, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2024/12/the-new-york-fed-dsge-model-forecast-december-2024/
BibTeX: View |
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the responsibility of the author(s).














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics