Anatomy of the Bank Runs in March 2023

Runs have plagued the banking system for centuries and returned to prominence with the bank failures in early 2023. In a traditional run—such as depicted in classic photos from the Great Depression—depositors line up in front of a bank to withdraw their cash. This is not how modern bank runs occur: today, depositors move money from a risky to a safe bank through electronic payment systems. In a recently published staff report, we use data on wholesale and retail payments to understand the bank run of March 2023. Which banks were run on? How were they different from other banks? And how did they respond to the run?
How (Un‑)Informed Are Depositors in a Banking Panic? A Lesson from History
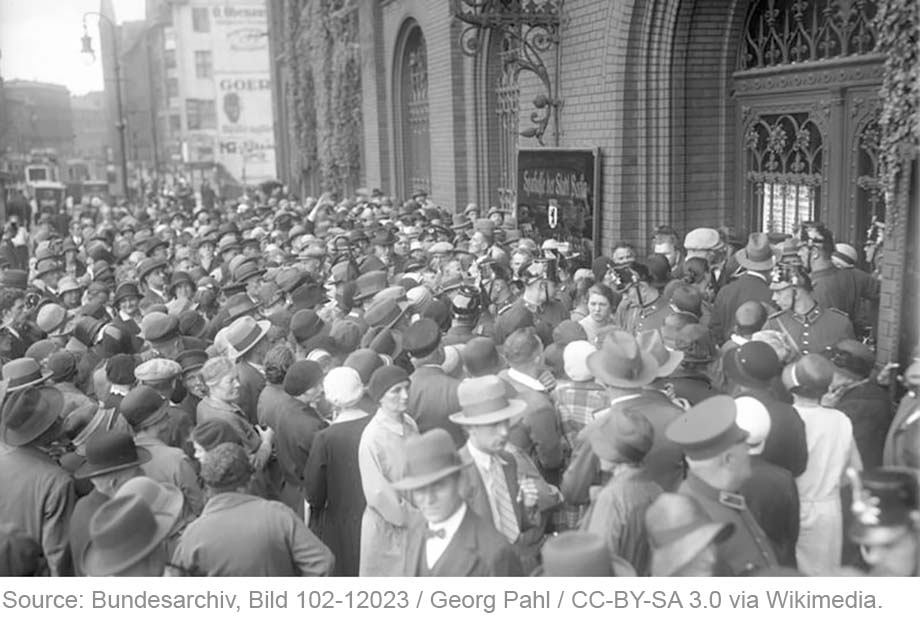

How informed or uninformed are bank depositors in a banking crisis? Can depositors anticipate which banks will fail? Understanding the behavior of depositors in financial crises is key to evaluating the policy measures, such as deposit insurance, designed to prevent them. But this is difficult in modern settings. The fact that bank runs are rare and deposit insurance universal implies that it is rare to be able to observe how depositors would behave in absence of the policy. Hence, as empiricists, we are lacking the counterfactual of depositor behavior during a run that is undistorted by the policy. In this blog post and the staff report on which it is based, we go back in history and study a bank run that took place in Germany in 1931 in the absence of deposit insurance for insight.
Cyberattacks and Supply Chain Disruptions
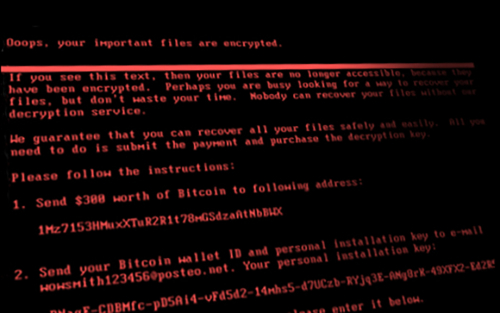
Cybercrime is one of the most pressing concerns for firms. Hackers perpetrate frequent but isolated ransomware attacks mostly for financial gains, while state-actors use more sophisticated techniques to obtain strategic information such as intellectual property and, in more extreme cases, to disrupt the operations of critical organizations. Thus, they can damage firms’ productive capacity, thereby potentially affecting their customers and suppliers. In this post, which is based on a related Staff Report, we study a particularly severe cyberattack that inadvertently spread beyond its original target and disrupted the operations of several firms around the world. More recent examples of disruptive cyberattacks include the ransomware attacks on Colonial Pipeline, the largest pipeline system for refined oil products in the U.S., and JBS, a global beef processing company. In both cases, operations halted for several days, causing protracted supply chain bottlenecks.
How Bank Reserves Are Distributed Matters. How You Measure Their Distribution Matters Too.
Changes in the distribution of banks’ reserve balances are important since they may impact conditions in the federal funds market and alter trading dynamics in money markets more generally. In this post, we propose using the Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient as a new approach to measuring reserve concentration. Since 2013, concentration, as captured by the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient, has co-moved with aggregate reserves, decreasing as aggregate reserves declined (such as in 2015-18) and increasing as aggregate reserves increased (such as at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic).
Crisis Chronicles: The Long Depression and the Panic of 1873

It always seemed to come down to railroads in the 1800s. Railroads fueled much of the economic growth in the United States at that time, but they required that a great deal of upfront capital be devoted to risky projects. The panics of 1837 and 1857 can both be pinned on railroad investments that went awry, creating enough doubt about the banking system to cause pervasive bank runs. The fatal spark for the Panic of 1873 was also tied to railroad investments—a major bank financing a railroad venture announced that it would suspend withdrawals. As other banks started failing, consumers and businesses pulled back and America entered what is recorded as the country’s longest depression.
Crisis Chronicles: Defensive Suspension and the Panic of 1857
Sometimes the world loses its bearings and the best alternative is a timeout.
Crisis Chronicles: The Man on the Twenty‑Dollar Bill and the Panic of 1837
Thomas Klitgaard and James Narron Correction: This post was updated on May 8 to correct the book title and spelling of the author’s name in the fifth paragraph. We regret the error. President Andrew Jackson was a “hard money” man. He saw specie—that is, gold and silver—as real money, and considered paper money a suspicious […]
Crisis Chronicles: The Panic of 1825 and the Most Fantastic Financial Swindle of All Time
Centered in London, the banking panic of 1825 has been called the first modern financial crisis, the first Latin American crisis, and the first emerging market crisis. And while the panic displayed many of the key elements of past crises we have covered—fluctuations in money growth, an investment bubble, a stock market crash, and bank runs—this crisis had its own twists, including a Bank of England that hesitated before stepping in as lender of last resort. But it is perhaps best known for an infamous bond market swindle surrounding an entirely made-up Central American principality. In this edition of Crisis Chronicles, we explore the Panic of 1825 and visit the mythical nation of Poyais.
Crisis Chronicles: The Panic of 1819—America’s First Great Economic Crisis
As we noted in our last post on the British crisis of 1816, while Britain emerged from nearly a quarter century of war with France ready to supply the world with manufactured goods, it needed cotton to supply the mills, and all of Europe needed wheat to supplement a series of poor harvests.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics