The Layers of Inflation Persistence

In a recent post, we introduced the Multivariate Core Trend (MCT), a measure of inflation persistence in the core sectors of the personal consumption expenditure (PCE) price index. With data up to February 2022, we used the MCT to interpret the nature of post-pandemic price spikes, arguing that inflation dynamics were dominated by a persistent component largely common across sectors, which we estimated at around 5 percent. Indeed, over the year, inflation proved to be persistent and broad based, and core PCE inflation is likely to end 2022 near 5 percent. So, what is the MCT telling us today? In this post, we extend our analysis to data through November 2022 and detect signs of a decline in the persistent component of inflation in recent data. We then dissect the layers of inflation persistence to fully understand that decline.
Global Supply Chain Pressure Index: May 2022 Update

Supply chain disruptions continue to be a major challenge as the world economy recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic. Furthermore, recent developments related to geopolitics and the pandemic (particularly in China) could put further strains on global supply chains. In a January post, we first presented the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index (GSCPI), a parsimonious global measure designed to capture supply chain disruptions using a range of indicators. We revisited our index in March, and today we are launching the GSCPI as a standalone product, with new readings to be published each month. In this post, we review GSCPI readings through April 2022 and briefly discuss the drivers of recent moves in the index.
A New Barometer of Global Supply Chain Pressures

Supply chain disruptions have become a major challenge for the global economy since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Factory shutdowns (particularly in Asia) and widespread lockdowns and mobility restrictions have resulted in disruptions across logistics networks, increases in shipping costs, and longer delivery times. Several measures have been used to gauge these disruptions, although those measures tend to focus on selected dimensions of global supply chains. In this post, we propose a new gauge, the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index (GSCPI), which integrates a number of commonly used metrics with an aim to provide a more comprehensive summary of potential disruptions affecting global supply chains.
High Import Prices along the Global Supply Chain Feed Through to U.S. Domestic Prices

The prices of U.S. imported goods, excluding fuel, have increased by 6 percent since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in February 2020. Around half of this increase is due to the substantial rise in the prices of imported industrial supplies, up nearly 30 percent. In this post, we consider the implications of the increase in import prices on U.S. industry inflation rates. In particular, we highlight how rising prices of imported intermediate inputs, like industrial supplies, can have amplified effects through the U.S. economy by increasing the production cost of goods that rely heavily on these inputs.
Cyberattacks and Supply Chain Disruptions
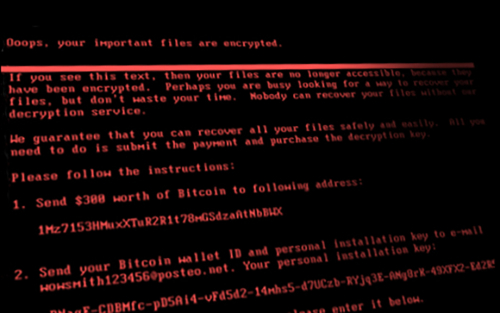
Cybercrime is one of the most pressing concerns for firms. Hackers perpetrate frequent but isolated ransomware attacks mostly for financial gains, while state-actors use more sophisticated techniques to obtain strategic information such as intellectual property and, in more extreme cases, to disrupt the operations of critical organizations. Thus, they can damage firms’ productive capacity, thereby potentially affecting their customers and suppliers. In this post, which is based on a related Staff Report, we study a particularly severe cyberattack that inadvertently spread beyond its original target and disrupted the operations of several firms around the world. More recent examples of disruptive cyberattacks include the ransomware attacks on Colonial Pipeline, the largest pipeline system for refined oil products in the U.S., and JBS, a global beef processing company. In both cases, operations halted for several days, causing protracted supply chain bottlenecks.
Endogenous Supply Chains, Productivity, and COVID‑19

During the COVID-19 pandemic, many industries adapted to new social distancing guidelines by adopting new technologies, providing protective equipment for their employees, and digitizing their methods of production. These changes in industries’ supply chains, together with monetary and fiscal stimulus, contributed to dampening the economic impact of COVID-19 over time. In this post, I discuss a new framework that analyzes how changes in supply chains can drive economic growth in the long run and mitigate recessions in the short run.
How Did China’s COVID‑19 Shutdown Affect U.S. Supply Chains?

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on trade between the United States and China so far. As workers became sick or were quarantined, factories temporarily closed, disrupting international supply chains. At the same time, the trade relationship between the United States and China has been characterized by rising protectionism and heightened trade policy uncertainty over the last few years. Against this background, this post examines how the recent period of economic disruptions in China has affected U.S. imports and discusses how this episode might impact firms’ supply chains going forward.
Why Renegotiating NAFTA Could Disrupt Supply Chains

Supply chains, where production of a final good incorporates specialized parts produced abroad, have become increasingly interlinked across the U.S.-Mexico border. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) allows tariff-free commerce between the United States, Canada, and Mexico, has facilitated this integration. Some critics of NAFTA are concerned about the bilateral trade deficit and have proposed stricter rules of origin (ROO), which would make it more cumbersome for firms to access the zero tariff rates they are entitled to with NAFTA. We argue that measures that make it costlier for U.S. firms to import will also hurt exports because much of U.S.-Mexican trade is part of global supply chains.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics