Is Work‑from‑Home Working?
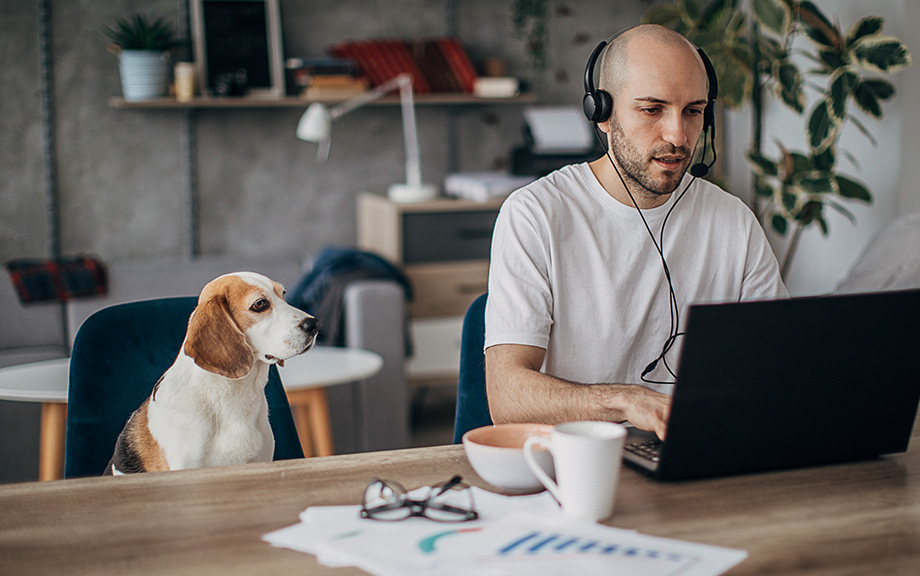

Though some offices have re-opened as the pandemic has receded, many workers have continued to work from home. Recent survey data suggest that workers would like more remote-work days than firms want to supply—a pattern that was evident even before the pandemic. Why have firms been so reluctant to offer remote work? And what will the recent seismic shift in remote work mean for the economy?
The New York Fed DSGE Model Forecast— June 2023

This post presents an update of the economic forecasts generated by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) model. We describe very briefly our forecast and its change since March 2023.
2023 State‑of‑the‑Field Conference on Cyber Risk to Financial Stability

The Federal Reserve Bank of New York and Columbia University’s School of International and Public Affairs (SIPA) co-organized the fourth annual State-of-the-Field Conferences on Cyber Risk to Financial Stability, on April 14, 2023. The conference builds on joint activity by the New York Fed and SIPA since 2017. Each year, the conference convenes panels to confront the same three questions: What are we learning about cyber risk to financial stability? What are we doing to improve resilience and stability? And what’s next? This blog post reviews some of these conversations from the 2023 conference.
How Do Firms Adjust Prices in a High Inflation Environment?

How do firms set prices? What factors do they consider, and to what extent are cost increases passed through to prices? While these are important questions in general, they become even more salient during periods of high inflation. In this blog post, we highlight preliminary results from ongoing research on firms’ price-setting behavior, a joint project between researchers at the Federal Reserve Banks of Atlanta, Cleveland, and New York. We use a combination of open-ended interviews and a quantitative survey in our analysis. Firms reported that the strength of demand was the most important factor affecting pricing decisions in recent years, while labor costs and maintaining steady profit margins were also highly important. Using three methodological approaches, we consistently estimate a rate of cost-price passthrough in the range of 60 percent for the representative firm over 2022-23—with considerable heterogeneity in this number across firms.
MCT Update: Inflation Persistence Declined Significantly in April

This post presents an updated estimate of inflation persistence, following the release of personal consumption expenditure (PCE) price data for April 2023. The estimates are obtained by the Multivariate Core Trend (MCT), a model we introduced on Liberty Street Economics last year and covered most recently in a May post. The MCT is a dynamic factor model estimated on monthly data for the seventeen major sectors of the PCE price index. It decomposes each sector’s inflation as the sum of a common trend, a sector-specific trend, a common transitory shock, and a sector-specific transitory shock. The trend in PCE inflation is constructed as the sum of the common and the sector-specific trends weighted by the expenditure shares.
What Drove Racial Disparities in the Paycheck Protection Program?

Numerous studies of the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), which provided loans to small businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic, have documented racial disparities in the program. Because publicly available PPP data only include information on approved loans, prior work has largely been unable to assess whether these disparities were driven by borrower application behavior or by lender approval decisions. In this post, which is based on a related Staff Report and NBER working paper, we use the Federal Reserve’s 2020 Small Business Credit Survey to examine PPP application behavior and approval decisions and to study the strengths and limitations of fintech lenders in enhancing access to credit for Black-owned businesses.
Do Economic Crises in Europe Affect the U.S.? Some Lessons from the Past Three Decades

In this post we summarize the main results of our contribution to a recent e-book, “The Making of the European Monetary Union: 30 years since the ERM crisis,” on the economic and financial crises in Europe since 1992-93, and focus on the spillovers of those crises onto the United States and the global economy. We find that the answer to the question in the title of this post is a (moderate) yes.
Measuring the Financial Stability Real Interest Rate, r**

Comparing our financial stability real interest rate, r** (“r-double-star”) with the prevailing real interest rate gives a measure of how vulnerable the economy is to financial instability. In this post, we first explain how r** can be measured, and then discuss its evolution over the last fifty years and how to interpret the recent banking turmoil within this framework.
Financial Stability and Interest Rates

In a recent research paper we argue that interest rates have very different consequences for current versus future financial stability. In the short run, lower real rates mean higher asset prices and hence higher net worth for financial institutions. In the long run, lower real rates lead intermediaries to shift their portfolios toward risky assets, making them more vulnerable over time. In this post, we use a model to highlight the challenging trade-offs faced by policymakers in setting interest rates.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics