New Dataset Maps Losses from Natural Disasters to the County Level

The Federal Reserve’s mission and regional structure ask that it always work to better understand local and regional economic activity. This requires gauging the economic impact of localized events, including natural disasters. Despite the economic significance of natural disasters—flowing often from their human toll—there are currently no publicly available data on the damages they cause in the United States at the county level.
The Nonbank Shadow of Banks

Financial and technological innovation and changes in the macroeconomic environment have led to the growth of nonbank financial institutions (NBFIs), and to the possible displacement of banks in the provision of traditional financial intermediation services (deposit taking, loan making, and facilitation of payments). In this post, we look at the joint evolution of banks—referred to as depository institutions from here on—and nonbanks inside the organizational structure of bank holding companies (BHCs). Using a unique database of the organizational structure of all BHCs ever in existence since the 1970s, we document the evolution of NBFI activities within BHCs. Our evidence suggests that there exist important conglomeration synergies to having both banks and NBFIs under the same organizational umbrella.
2023 State‑of‑the‑Field Conference on Cyber Risk to Financial Stability

The Federal Reserve Bank of New York and Columbia University’s School of International and Public Affairs (SIPA) co-organized the fourth annual State-of-the-Field Conferences on Cyber Risk to Financial Stability, on April 14, 2023. The conference builds on joint activity by the New York Fed and SIPA since 2017. Each year, the conference convenes panels to confront the same three questions: What are we learning about cyber risk to financial stability? What are we doing to improve resilience and stability? And what’s next? This blog post reviews some of these conversations from the 2023 conference.
Banking System Vulnerability: 2022 Update

To assess the vulnerability of the U.S. financial system, it is important to monitor leverage and funding risks—both individually and in tandem. In this post, we provide an update of four analytical models aimed at capturing different aspects of banking system vulnerability with data through 2022:Q2, assessing how these vulnerabilities have changed since last year. The four models were introduced in a Liberty Street Economics post in 2018 and have been updated annually since then.
Cyberattacks and Supply Chain Disruptions
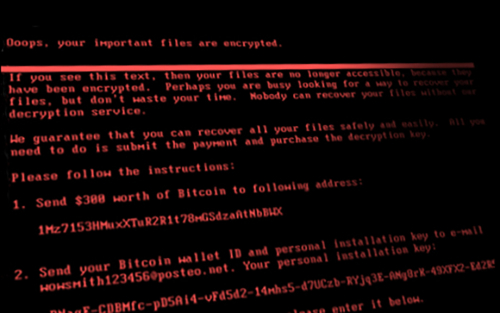
Cybercrime is one of the most pressing concerns for firms. Hackers perpetrate frequent but isolated ransomware attacks mostly for financial gains, while state-actors use more sophisticated techniques to obtain strategic information such as intellectual property and, in more extreme cases, to disrupt the operations of critical organizations. Thus, they can damage firms’ productive capacity, thereby potentially affecting their customers and suppliers. In this post, which is based on a related Staff Report, we study a particularly severe cyberattack that inadvertently spread beyond its original target and disrupted the operations of several firms around the world. More recent examples of disruptive cyberattacks include the ransomware attacks on Colonial Pipeline, the largest pipeline system for refined oil products in the U.S., and JBS, a global beef processing company. In both cases, operations halted for several days, causing protracted supply chain bottlenecks.
Did Subsidies to Too‑Big‑To‑Fail Banks Increase during the COVID‑19 Pandemic?

New Liberty Street Economics analysis by Asani Sarkar investigates whether the COVID-19 pandemic has led to an increase in implicit TBTF subsidies for large firms.
Did Too‑Big‑To‑Fail Reforms Work Globally?

Once a bank grows beyond a certain size or becomes too complex and interconnected, investors often perceive that it is “too big to fail” (TBTF), meaning that if the bank were to fail, the government would likely bail it out. Following the global financial crisis (GFC) of 2008, the G20 countries agreed on a set of reforms to eliminate the perception of TBTF, as part of a broader package to enhance financial stability. In June 2020, the Financial Stability Board (FSB; a 68-member international advisory body set up in 2009) published the results of a year-long evaluation of the effectiveness of TBTF reforms. In this post, I discuss the main conclusions of the report—in particular, the finding that implicit funding subsidies to global banks have decreased since the implementation of reforms but remain at levels comparable to the pre-crisis period.
The Primary Dealer Credit Facility

On March 17, 2020, the Federal Reserve announced that it would re-establish the Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF) to allow primary dealers to support smooth market functioning and facilitate the availability of credit to businesses and households. The PDCF started offering overnight and term funding with maturities of up to ninety days on March 20. It will be in place for at least six months and may be extended as conditions warrant. In this post, we provide an overview of the PDCF and its usage to date.
Hey, Economist! Tobias Adrian Reflects on His Work at the N.Y. Fed before Heading to the IMF

Tobias Adrian is leaving the New York Fed to become the Financial Counselor and Director of the Monetary and Capital Markets Department at the International Monetary Fund (IMF). In announcing Adrian’s appointment, Christine Lagarde, managing director of the IMF, described Tobias as “internationally highly regarded for his insightful analytical work.” Until he starts his new position at the beginning of 2017, Adrian will be winding down his service as Senior Vice President of the New York Fed and Associate Director of the Bank’s Research and Statistics Group. Before he moves on to the IMF, Adrian shared some insight on his time at the Bank.












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics