Long COVID Appears to Have Led to a Surge of the Disabled in the Workplace

Although most of those infected with COVID-19 have recovered relatively quickly, a substantial share has not, and remains symptomatic months or even years later, in what is commonly referred to as long COVID. Data on the incidence of long COVID is scarce, but recent Census Bureau data suggest that sixteen million working age Americans suffer from it. The economic costs of long COVID is estimated to be in the trillions. While many with long COVID have dropped out of the labor force because they can no longer work, many others appear to be working despite having disabilities related to the disease. Indeed, there has been an increase of around 1.7 million disabled persons in the U.S. since the pandemic began, and there are close to one million newly disabled workers. These disabled workers can benefit from workplace accommodations to help them remain productive and stay on the job, particularly as the majority deal with fatigue and brain fog, the hallmarks of long COVID.
Revisiting Federal Student Loan Forgiveness: An Update Based on the White House Plan

On August 24, 2022, the White House released a plan to cancel federal student loans for most borrowers. In April, we wrote about the costs and who most benefits from a few hypothetical loan forgiveness proposals using our Consumer Credit Panel, based on Equifax credit report data. In this post, we update our framework to consider the White House plan now that parameters are known, with estimates for the total amount of forgiven loans and the distribution of who holds federal student loans before and after the proposed debt jubilee.
Small Business Recovery after Natural Disasters
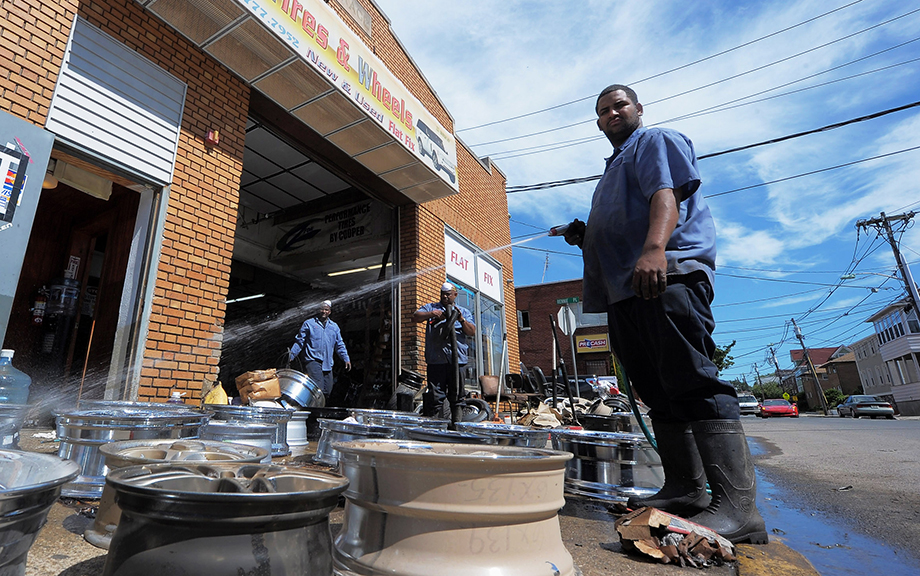

The first post of this series found that small businesses owned by people of color are particularly vulnerable to natural disasters. In this post, we focus on the aftermath of disasters, and examine disparities in the ability of firms to reopen their businesses and access disaster relief. Our results indicate that Black-owned firms are more likely to remain closed for longer periods and face greater difficulties in obtaining the immediate relief needed to cope with a natural disaster.
How Do Natural Disasters Affect U.S. Small Business Owners?

Recent research has linked climate change and socioeconomic inequality (see here, here, and here). But what are the effects of climate change on small businesses, particularly those owned by people of color, which tend to be more resource-constrained and less resilient? In a series of two posts, we use the Federal Reserve’s Small Business Credit Survey (SBCS) to document small businesses’ experiences with natural disasters and how these experiences differ based on the race and ethnicity of business owners. This first post shows that small firms owned by people of color sustain losses from natural disasters at a disproportionately higher rate than other small businesses, and that these losses make up a larger portion of their total revenues. In the second post, we explore the ability of small firms to reopen and to obtain disaster relief funding in the aftermath of climate events.
The Adverse Effect of “Mandatory” Flood Insurance on Access to Credit
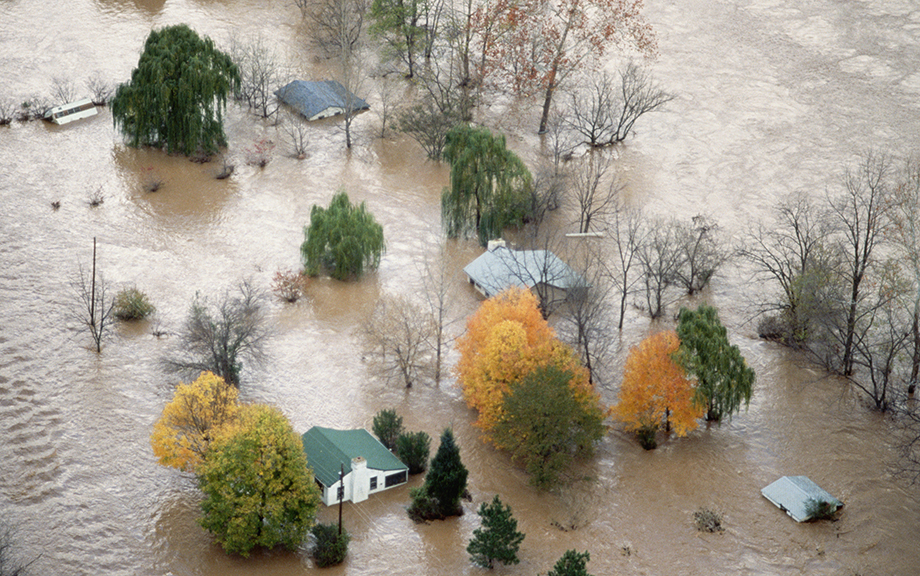

The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) was designed to reduce household and lender flood-risk exposure and “encourage lending.” In this post, which is based on our related study, we show that in certain situations the program actually limits access to credit, particularly for low-income borrowers—an unintended consequence of this well-intentioned program.















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Follow Liberty Street Economics
Follow Liberty Street Economics